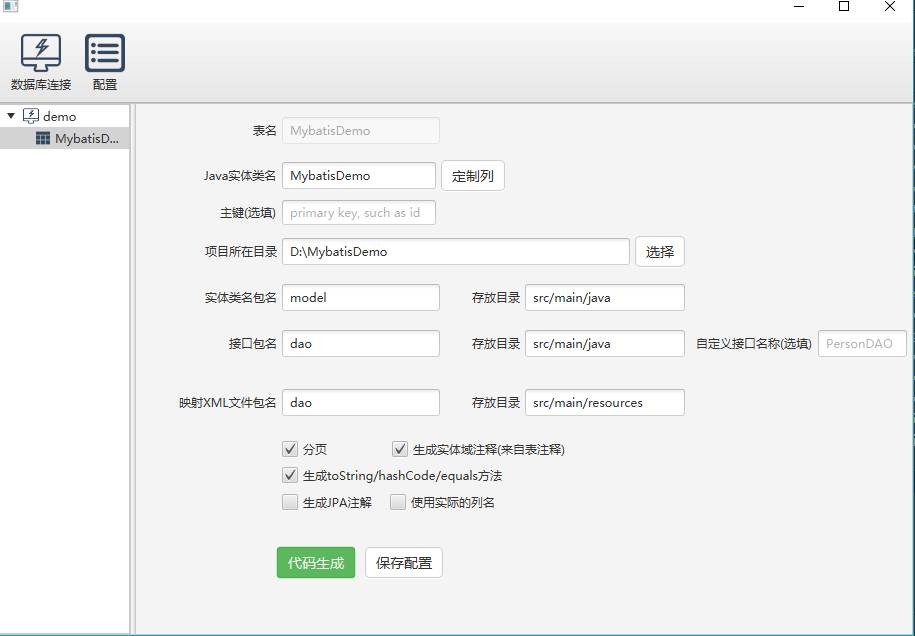
今天完成的事
学习了一下自动生成。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<!-- classPathEntry:数据库的JDBC驱动的jar包地址 -->
<classPathEntry location="C:\Users\sony\.m2\repository\mysql\mysql-connector-java\5.1.38\mysql-connector-java-5.1.38.jar" />
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<commentGenerator>
<!-- 抑制警告 -->
<property name="suppressTypeWarnings" value="true" />
<!-- 是否去除自动生成的注释 true:是 : false:否 -->
<property name="suppressAllComments" value="false" />
<!-- 是否生成注释代时间戳-->
<property name="suppressDate" value="true" />
</commentGenerator>
<!--数据库连接的信息:驱动类、连接地址、用户名、密码 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://47.95.7.57:3306/demo" userId="root"
password="Gao4651016">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- 默认false,把JDBC DECIMAL 和 NUMERIC 类型解析为 Integer true,把JDBC DECIMAL 和
NUMERIC 类型解析为java.math.BigDecimal -->
<!-- <javaTypeResolver>
<property name="forceBigDecimals" value="false" />
</javaTypeResolver> -->
<!--生成Model类存放位置 -->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="model"
targetProject="D:\MybatisDemo\src\main\java">
<!-- 是否在当前路径下新加一层schema,eg:fase路径com.oop.eksp.user.model, true:com.oop.eksp.user.model.[schemaName] -->
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false" />
<!-- 是否针对string类型的字段在set的时候进行trim调用 -->
<property name="trimStrings" value="true" />
</javaModelGenerator>
<!--生成映射文件存放位置 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="dao"
targetProject="D:\MybatisDemo\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!--生成Dao类存放位置 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER"
targetPackage="dao" targetProject="D:\MybatisDemo\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true" />
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- tableName:用于自动生成代码的数据库表;domainObjectName:对应于数据库表的javaBean类名 -->
<table schema="general" tableName="MybatisDemo" domainObjectName="User">
<!--domain字段的命名规则,false:默认为驼峰命名 true:按数据库真实命名 -->
<property name="useActualColumnNames" value="false"/>
<!-- 忽略列,不生成bean 字段 -->
<!-- <ignoreColumn column="FRED" /> -->
<!-- 指定列的java数据类型 -->
<!-- <columnOverride column="LONG_VARCHAR_FIELD" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> -->
</table>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
第二种方法
收获
脏读、幻读、不可重复读
1.脏读:
脏读就是指当一个事务正在访问数据,并且对数据进行了修改,而这种修改还没有提交到数据库中,这时,另外一个事务也访问这个数据,然后使用了这个数据。
2.不可重复读:
是指在一个事务内,多次读同一数据。在这个事务还没有结束时,另外一个事务也访问该同一数据。那么,在第一个事务中的两次读数据之间,由于第二个事务的修改,那么第一个事务两次读到的的数据可能是不一样的。这样就发生了在一个事务内两次读到的数据是不一样的,因此称为是不可重复读。(即不能读到相同的数据内容)
例如,一个编辑人员两次读取同一文档,但在两次读取之间,作者重写了该文档。当编辑人员第二次读取文档时,文档已更改。原始读取不可重复。如果只有在作者全部完成编写后编辑人员才可以读取文档,则可以避免该问题。
3.幻读:
是指当事务不是独立执行时发生的一种现象,例如第一个事务对一个表中的数据进行了修改,这种修改涉及到表中的全部数据行。同时,第二个事务也修改这个表中的数据,这种修改是向表中插入一行新数据。那么,以后就会发生操作第一个事务的用户发现表中还有没有修改的数据行,就好象
发生了幻觉一样。
例如,一个编辑人员更改作者提交的文档,但当生产部门将其更改内容合并到该文档的主复本时,发现作者已将未编辑的新材料添加到该文档中。如果在编辑人员和生产部门完成对原始文档的处理之前,任何人都不能将新材料添加到文档中,则可以避免该问题。
研究了一下mybatis的动态代理实现
我把关于getMapper方法的实现方式理解为动态代理。是一个AOP思想的实现。从源码上我们可以看到getMapper方法会去调用Configuration类的getMapper方法。好了。一切的开始都在这里了。
DefaultSqlSession类:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
对于Configuration类上一章里面就说明他里面存放了所有关于XML文件的配置信息。从参数上我们可以看到他要我们传入一个Class<T>类型。这已经可以看到后面一定要用到反射机制和动态生成相应的类实例。让我们进一步查看一下源码。
Configuration类:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import org.apache.ibatis.builder.annotation.MapperAnnotationBuilder;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.ResolverUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
//这个类通过名字就可以看出 是用来注册Mapper接口与获取生成代理类实例的工具类
public class MapperRegistry {
//全局配置文件对象
private Configuration config;
//一个HashMap Key是mapper的类型对象, Value是MapperProxyFactory对象
//这个MapperProxyFactory是创建Mapper代理对象的工厂 我们一会在分析
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
//获取生成的代理对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//通过Mapper的接口类型 去Map当中查找 如果为空就抛异常
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null)
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
try {
//否则创建一个当前接口的代理对象 并且传入sqlSession
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
//注册Mapper接口
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
public Collection<Class<?>> getMappers() {
return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(knownMappers.keySet());
}
ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<Class<?>>();
resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName);
Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses();
for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) {
addMapper(mapperClass);
}
}
//通过包名扫描下面所有接口
public void addMappers(String packageName) {
addMappers(packageName, Object.class);
}
}
MapperRegistry
当我点击进来发现他又调用MapperRegistry类的getMapper方法的时候,心里面有一种又恨又爱的冲动——这就是构架之美和复杂之恨。MapperRegistry类我把他理解存放动态代理工厂(MapperProxyFactory类)的库存。当然我们还是进去看一看源码吧。
MapperRegistry类:
1 public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
2 final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
3 if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
4 throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
5 }
6 try {
7 return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
8 } catch (Exception e) {
9 throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
10 }
11 }
好了。看到这一段代码的时候都明白——MapperRegistry类就是用来存放MapperProxyFactory类的。我们还是在看一下knownMappers成员是一个什么要样子的集合类型。
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
knownMappers是一个字典类型。从Key的类型上我们可以判断出来是一个类一个动态代理工厂。笔者看到这里的时候都会去点击一个MapperProxyFactory类的源码。看看他里面又是一些什么东东。
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
//这个类负责创建具体Mapper接口代理对象的工厂类
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
//具体Mapper接口的Class对象
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
//该接口下面方法的缓存 key是方法对象 value是对接口中方法对象的封装
private Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
//构造参数没啥好说的
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//创建了一个代理类并返回
//关于Proxy的API 可以查看java官方的API
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
//在这里传入sqlSession 创建一个Mapper接口的代理类
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
//在这里创建了MapperProxy对象 这个类实现了JDK的动态代理接口 InvocationHandler
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
//调用上面的方法 返回一个接口的代理类
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxyFactory
还好。代码不是很多,理解起来也不是很复杂。略看一下源码,一个类,一个动态代理工厂,多个方法代理。我们先把猜测放在这里,然后让我们回到上面部分吧。我们发现MapperRegistry类的getMapper方法里面最后会去调用MapperProxyFactory类的newInstance方法。这个时候我们又看到他实例化了一个MapperProxy类。MapperProxy类是什么。这个就关系到Proxy类的用法了。所以去查看相关资料了。意思明显每执行一次XxxMapper例子里面的IProductMapper接口)的方法都会创建一个MapperProxy类。方法执行之前都会先去调用相应MapperProxy类里面的invoke方法。如下
MapperProxy类:
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
//实现了JDK动态代理的接口 InvocationHandler
//在invoke方法中实现了代理方法调用的细节
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
//SqlSession
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
//接口的类型对象
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
//接口中方法的缓存 有MapperProxyFactory传递过来的。
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
//构造参数
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//接口代理对象所有的方法调用 都会调用该方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//判断是不是基础方法 比如toString() hashCode()等,这些方法直接调用不需要处理
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
}
//这里进行缓存
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//调用mapperMethod.execute 核心的地方就在这个方法里,这个方法对才是真正对SqlSession进行的包装调用
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
//缓存处理
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}
MapperPro
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.*;
//这个类是整个代理机制的核心类,对Sqlsession当中的操作进行了封装
public class MapperMethod {
//一个内部封 封装了SQL标签的类型 insert update delete select
private final SqlCommand command;
//一个内部类 封装了方法的参数信息 返回类型信息等
private final MethodSignature method;
//构造参数
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, method);
}
//这个方法是对SqlSession的包装调用
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
//定义返回结果
Object result;
//如果是INSERT操作
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
//处理参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//调用sqlSession的insert方法
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
//如果是UPDATE操作 同上
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
//如果是DELETE操作 同上
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
//如果是SELECT操作 那么情况会多一些 但是也都和sqlSession的查询方法一一对应
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
//如果返回void 并且参数有resultHandler
//则调用 void select(String statement, Object parameter, ResultHandler handler);方法
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
//如果返回多行结果这调用 <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
//executeForMany这个方法调用的
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
//如果返回类型是MAP 则调用executeForMap方法
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
//否则就是查询单个对象
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else {
//如果全都不匹配 说明mapper中定义的方法不对
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
//如果返回值为空 并且方法返回值类型是基础类型 并且不是VOID 则抛出异常
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) {
final Object result;
if (method.returnsVoid()) {
result = null;
} else if (Integer.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Integer.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = rowCount;
} else if (Long.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Long.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = (long) rowCount;
} else if (Boolean.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Boolean.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = (rowCount > 0);
} else {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + method.getReturnType());
}
return result;
}
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());
if (void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) {
throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName()
+ " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation,"
+ " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");
}
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args));
} else {
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args));
}
}
//返回多行结果 调用sqlSession.selectList方法
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//如果参数含有rowBounds则调用分页的查询
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
//没有分页则调用普通查询
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
private <E> Object convertToDeclaredCollection(Configuration config, List<E> list) {
Object collection = config.getObjectFactory().create(method.getReturnType());
MetaObject metaObject = config.newMetaObject(collection);
metaObject.addAll(list);
return collection;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <E> E[] convertToArray(List<E> list) {
E[] array = (E[]) Array.newInstance(method.getReturnType().getComponentType(), list.size());
array = list.toArray(array);
return array;
}
private <K, V> Map<K, V> executeForMap(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Map<K, V> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey(), rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey());
}
return result;
}
public static class ParamMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2212268410512043556L;
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
if (!super.containsKey(key)) {
throw new BindingException("Parameter '" + key + "' not found. Available parameters are " + keySet());
}
return super.get(key);
}
}
从源码的意思:从缓存中获得执行方法对应的MapperMethod类实例。如果MapperMethod类实例不存在的情况,创建加入缓存并返回相关的实例。最后调用MapperMethod类的execute方法。
到这里小结一下,上面讲到笔者例子里面用到的getMapper方法。getMapper方法就是用来获得相关的数据操作类接口。而事实数据操作类邦定了动态代理。所以操据操作类执行方法的时候,会触动每个方法相应的MapperProxy类的invoke方法。所以invoke方法返回的结果就是操据操作类执行方法的结果。这样子我们就知道最后的任务交给了MapperMethod类实例。
MapperMethod类里面有俩个成员:SqlCommand类和MethodSignature类。从名字上我们大概的能想到一个可能跟SQL语句有关系,一个可能跟要执行的方法有关系。事实也是如此。笔者查看了SqlCommand类的源码。确切来讲这一部分的内容跟XxxMapper的XML配置文件里面的select节点、delete节点等有关。我们都会知道节点上有id属性值。那么MyBatis框架会把每一个节点(如:select节点、delete节点)生成一个MappedStatement类。要找到MappedStatement类就必须通过id来获得。有一个细节要注意:代码用到的id = 当前接口类 + XML文件的节点的ID属性。如下
//一个内部类 封装了具体执行的动作
public static class SqlCommand {
//xml标签的id
private final String name;
//insert update delete select的具体类型
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) throws BindingException {
//拿到全名 比如 org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper.selectBlog
String statementName = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
MappedStatement ms = null;
//获取MappedStatement对象 这个对象封装了XML当中一个标签的所有信息 比如下面
//<select id="selectBlog" resultType="Blog">
//select * from Blog where id = #{id}
//</select>
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementName)) {
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statementName);
} else if (!mapperInterface.equals(method.getDeclaringClass().getName())) { // 这里是一个BUG
String parentStatementName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName();
if (configuration.hasStatement(parentStatementName)) {
ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(parentStatementName);
}
}
//为空抛出异常
if (ms == null) {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): " + statementName);
}
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
//判断SQL标签类型 未知就抛异常
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public SqlCommandType getType() {
return type;
}
}
//内部类 封装了接口当中方法的 参数类型 返回值类型 等信息
public static class MethodSignature {
//是否返回多调结果
private final boolean returnsMany;
//返回值是否是MAP
private final boolean returnsMap;
//返回值是否是VOID
private final boolean returnsVoid;
//返回值类型
private final Class<?> returnType;
//mapKey
private final String mapKey;
//resultHandler类型参数的位置
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
//rowBound类型参数的位置
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
//用来存放参数信息
private final SortedMap<Integer, String> params;
//是否存在命名参数
private final boolean hasNamedParameters;
//在这里对上面的属性进行初始化 就不一一详细说明了 具体实现细节可以看下面的代码。
public MethodSignature(Configuration configuration, Method method) throws BindingException {
this.returnType = method.getReturnType();
this.returnsVoid = void.class.equals(this.returnType);
this.returnsMany = (configuration.getObjectFactory().isCollection(this.returnType) || this.returnType.isArray());
this.mapKey = getMapKey(method);
this.returnsMap = (this.mapKey != null);
this.hasNamedParameters = hasNamedParams(method);
this.rowBoundsIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, RowBounds.class);
this.resultHandlerIndex = getUniqueParamIndex(method, ResultHandler.class);
this.params = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(getParams(method, this.hasNamedParameters));
}
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = params.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
} else if (!hasNamedParameters && paramCount == 1) {
return args[params.keySet().iterator().next()];
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// issue #71, add param names as param1, param2...but ensure backward compatibility
final String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1);
if (!param.containsKey(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
public boolean hasRowBounds() {
return (rowBoundsIndex != null);
}
public RowBounds extractRowBounds(Object[] args) {
return (hasRowBounds() ? (RowBounds) args[rowBoundsIndex] : null);
}
public boolean hasResultHandler() {
return (resultHandlerIndex != null);
}
public ResultHandler extractResultHandler(Object[] args) {
return (hasResultHandler() ? (ResultHandler) args[resultHandlerIndex] : null);
}
public String getMapKey() {
return mapKey;
}
public Class<?> getReturnType() {
return returnType;
}
public boolean returnsMany() {
return returnsMany;
}
public boolean returnsMap() {
return returnsMap;
}
public boolean returnsVoid() {
return returnsVoid;
}
private Integer getUniqueParamIndex(Method method, Class<?> paramType) {
Integer index = null;
final Class<?>[] argTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) {
if (paramType.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i])) {
if (index == null) {
index = i;
} else {
throw new BindingException(method.getName() + " cannot have multiple " + paramType.getSimpleName() + " parameters");
}
}
}
return index;
}
private String getMapKey(Method method) {
String mapKey = null;
if (Map.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getReturnType())) {
final MapKey mapKeyAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(MapKey.class);
if (mapKeyAnnotation != null) {
mapKey = mapKeyAnnotation.value();
}
}
return mapKey;
}
private SortedMap<Integer, String> getParams(Method method, boolean hasNamedParameters) {
final SortedMap<Integer, String> params = new TreeMap<Integer, String>();
final Class<?>[] argTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
for (int i = 0; i < argTypes.length; i++) {
if (!RowBounds.class.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i]) && !ResultHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(argTypes[i])) {
String paramName = String.valueOf(params.size());
if (hasNamedParameters) {
paramName = getParamNameFromAnnotation(method, i, paramName);
}
params.put(i, paramName);
}
}
return params;
}
private String getParamNameFromAnnotation(Method method, int i, String paramName) {
final Object[] paramAnnos = method.getParameterAnnotations()[i];
for (Object paramAnno : paramAnnos) {
if (paramAnno instanceof Param) {
paramName = ((Param) paramAnno).value();
}
}
return paramName;
}
private boolean hasNamedParams(Method method) {
boolean hasNamedParams = false;
final Object[][] paramAnnos = method.getParameterAnnotations();
for (Object[] paramAnno : paramAnnos) {
for (Object aParamAnno : paramAnno) {
if (aParamAnno instanceof Param) {
hasNamedParams = true;
break;
}
}
}
return hasNamedParams;
}
}
}
MapperMethod
看到这里的时候,我们就可以回头去找一找在什么时候增加了MappedStatement类。上面之所以可以执行是建立在XML配置信息都被加载进来了。所以MappedStatement类也一定是在加载配置的时候就进行的。自行查看一下MapperBuilderAssistant类的addMappedStatement方法——加深理解。SqlCommand类的name成员和type成员我们还是关注一下。name成员就是节点的ID,type成员表示查寻还是更新或是删除。至于MethodSignature类呢。他用于说明方法的一些信息,主要有返回信息。
上面讲了这多一点主要是为了查看execute方法源码容易一点。因为execute方法都要用到SqlCommand类和MethodSignature类。
1 public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
2 Object result;
3 switch (command.getType()) {
4 case INSERT: {
5 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
6 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
7 break;
8 }
9 case UPDATE: {
10 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
11 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
12 break;
13 }
14 case DELETE: {
15 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
16 result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
17 break;
18 }
19 case SELECT:
20 if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
21 executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
22 result = null;
23 } else if (method.returnsMany()) {
24 result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
25 } else if (method.returnsMap()) {
26 result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
27 } else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
28 result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
29 } else {
30 Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
31 result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
32 }
33 break;
34 case FLUSH:
35 result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
36 break;
37 default:
38 throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
39 }
40 if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
41 throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
42 + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
43 }
44 return result;
45 }
重点部分就是这里,我们会发现我们转了一圈,最后还是要回到SqlSession接口实例上。完美的一圈!
看到了这里我们就清楚调头去看一下SqlSession接口实例吧。
遇到的问题
每一次mybatis不提交。主键会自增,是为什么呢。
因为mysql默认采用的是innodb引擎。
这个引擎里面的auto_increament的计数器记录的当前值是保存在存内存中的,并不是存在于磁盘上。
当mysqlserver处于运行的时候,这个计数值只会随着insert改增长,不会随着delete而减少。而当mysql
server启动时,当我们需要去查询auto_increment计数值时,mysql便会自动执行:SELECT MAX(id) FROM 表名
FOR UPDATE;语句来获得当前auto_increment列的最大值,然后将这个值放到auto_increment计数器中。所以就算
Rollback MySQL的auto_increament计数器也不会作负运算。
所以我不提交,但是内存中auto_increament也会+1。
明天的计划
学习






评论