发表于: 2017-12-08 22:14:23
1 760
今天完成的事情:
对AOP进行代码实操作:
AOP切面编程本身不仅仅应用在Spring中,Spring对AOP的支持仅仅覆盖了最基础的应用,
我们所能做的只能使用切面的方法去对被通知类进行切割,并不能使用属性或者构造去切割,在AspectJ框架
中是可以的. 另外AOP这个概念,我们在反射的学习中早已经接触过,那个有点抽象,我后面再补充学习.
水了2天日报,总算有一点点干货..
首先还是最新的,脱离XML配置的,使用Java pojo作为配置类. Annotation(注解)
package com.myspring.aop.annotation;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
/**
* @author Arike
* Create_at 2017/12/7 15:11
*/
@Configuration()
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.myspring.aop.annotation"})
public class AopConfig {
}
这个配置和基础的config类唯一的区别就是需要显示的打开切面自动代理.
使用了
@Configuration 标签代表该类是作为Spring基础配置类
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy标签代表打开切面自动代理
@ComponentScan(.....)标签规定了这个配置类去具体的哪个包里面扫描组件
对比Spring 老版本所支持的xml配置是真的便捷.
下面是被通知类(被切割)
package com.myspring.aop.annotation;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author Arike
* Create_at 2017/12/7 15:12
*/
@Component
@Data
public class Run {
public void circle() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.print("1");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
被通知类并不需要做太多的修改以及注释.
仅仅只需要和没有AOP的情况的@Component(组件)注解而已
Aspect切面类(通知类)
package com.myspring.aop.annotation;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Required;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* @author Arike
* Create_at 2017/12/7 15:10
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class TimeCount {
private long timebegin ;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.myspring.aop.annotation.Run.circle(..))")
public void circles() {
}
@Before("circles()")
public void start() {
timebegin = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
@After("circles()")
public void end() {
System.out.println("总耗时" + ((double)System.currentTimeMillis() - timebegin)/1000+"毫秒");
}
}
@Aspect 注解表示该类是作为一个切面类,这也就算是注解的精髓了,一个标签就很直白赋予了他该拥有的功能.
@Pointcut("execution(* com.myspring.aop.annotation.Run.circle(..))")
public void circles() {
}
@Pointcut标签表示切入点,SpringAOP这块儿仅仅只能以方法为作为被通知目标,所以切入点应该以方法结尾.
另外关于execution执行语句的意思.
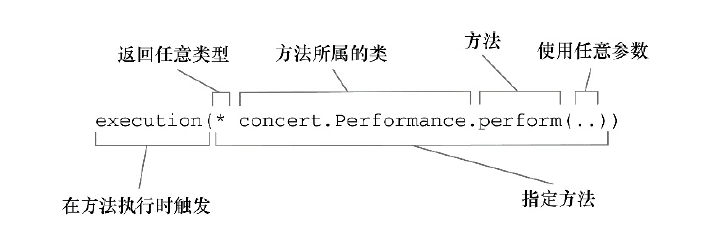
这个图给了很具体的解释了.
注解下面声明的一个没有返回值的方法
public void circles() {
}
是为了给这个切入点取一个别名,便于我们要切入的方法使用.
@before @after 表示在切入点之前通知和切入点之后通知.
嗯,AOP JavaConfig配置大致就是这个流程,
使用XML配置.
使用XML配置和JavaConfig配置的区别就在于XML不需要注解,另外这里需要注意的是AOP和Bean类的区别,
Bean类可以混合使用XML和annotation,而AOP只能选择其中一种,要么全部在XML中,要么全部使用Annotation.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd ">
<bean id="run" class="com.myspring.aop.xml.Run"/>
<bean id="timecount" class="com.myspring.aop.xml.TimeCount"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="timecount">
<aop:pointcut id="circle" expression="execution(* com.myspring.aop.xml.Run.circle(..))"/>
<aop:before
pointcut-ref="circle"
method="start"/>
<aop:after
pointcut-ref="circle"
method="end"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
package com.myspring.aop.xml;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author Arike
* Create_at 2017/12/7 15:12
*/
@Component
@Data
public class Run {
public void circle() {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.print("1");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
package com.myspring.aop.xml;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author Arike
* Create_at 2017/12/7 15:10
*/
@Component
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class TimeCount {
private long timebegin;
public void start() {
timebegin = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public void end() {
System.out.println("总耗时" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - timebegin)+"毫秒");
}
}
明天计划的事情:
SpringMVC的第一个项目和部署到tomcat做今天也完成了,为了不让日报冗长,明天一起更.
明天计划将任务一的做的数据库的操作部署到tomcat.
遇到的问题:
看了很多的博客和网站基础教程.发现对Spring的讲解都不是很好,
折腾一天才搞出一个基础项目,自己查询资料的能力有待提升.
收获:
学会了tomcat的部署以以及应用. AOP,MVC基础知识.





评论