发表于: 2017-11-12 21:28:49
1 859
今天完成的事情
配置redis的连接池
Jedis对象并不是线程安全的,在多线程下使用同一个Jedis对象会出现并发问题,为了避免每次使用Jedis对象时都需要重新构建,Jedis提供了JedisPool,JedisPool时基于Commons Pool 2实现的一个线程安全的连接池,所以不需要引入新的jar包
建立一个类,用于建立连接池,提供jedis实例
public class RedisClient {
private static String IP = "127.0.0.1";
private static int PORT = 6379;
private static int MAX_IDLE = 200;
private static int MAX_WAIT = 10000;
private static int TIMEOUT = 10000;
private static boolean TEST_ON_BORROW = true;
private static JedisPool jedisPool = null;
/**
* 初始化连接池
*/
static {
JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig();
config.setMaxIdle(MAX_IDLE);
config.setMaxWaitMillis(MAX_WAIT);
config.setTestOnBorrow(TEST_ON_BORROW);
jedisPool = new JedisPool(config,IP,PORT,TIMEOUT);
}
/**
* 获取Jedis实例
* @return
*/
public static Jedis getJedis(){
if (jedisPool!=null){
Jedis resource = jedisPool.getResource();
return resource;
}else
return null;
}
/**
* 释放jedis资源
* @param jedis
*/
public static void returnResource (final Jedis jedis){
if (jedis!=null)
jedisPool.returnResource(jedis);
}
}
配置数据库的常规操作,IP地址,端口号,最大连接数,等待时间等
getJedis()方法用于提供配置好连接池的Jedis实例,以供调用者使用
进行测试
@org.junit.Test
public void testredispool(){
Jedis jedis = RedisClient.getJedis();
jedis.sadd("test11","hello world");
}
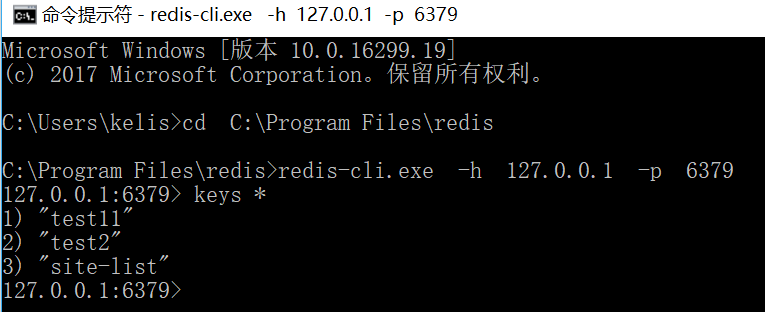
在cmd中查看是否存在:
确实存在,说明插入成功
尝试添加对象到redis中
需要自己编写序列化和反序列化的工具类:
public class SerializeUtil序列化方法:
/**
* 序列化
* @param object
* @return
*/
public static byte[] serialze(Object object){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
byte[] bytes = new byte[0];
try {
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(object);
bytes = baos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
采用输入流方法将对象转换为字节数组
反序列化方法:
/**
* 反序列化
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static Object unserialze(byte[] bytes){
ByteArrayInputStream bais = null;
bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
try {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bais);
return ois.readObject();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
采用输出流方法将字节数组转换为Object对象
进行测试,添加对象,先序列化再添加:
@org.junit.Test
public void redis11(){
Jedis jedis = RedisClient.getJedis();
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("hello");
jedis.set(stu.getName().getBytes(), SerializeUtil.serialze(stu));
}
然后根据key hello获取value,反序列化为Object对象,再强制转换为Student对象
@org.junit.Test
public void redis_get(){
Jedis jedis = RedisClient.getJedis();
Student s = (Student) SerializeUtil.unserialze(jedis.get("hello".getBytes()));
System.out.println(s);
}
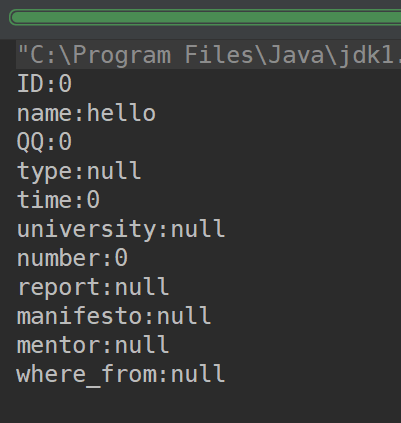
打印输出:
测试成功
明天的计划
用nginx配置负载均衡,压测
遇到的问题
无
收获
了解了序列化和反序列化的相关知识





评论