发表于: 2017-10-29 13:44:36
1 876
day10
今日完成
在spring容器内拼凑bean叫作装配。装配bean的时候,你是在告诉容器,需要哪些bean,以及容器如何使用依赖注入将它们配合在一起。理论上,bean装配可以从任何资源获得,包括属性文件,关系数据库等,但xml是最常见的spring 应用系统配置源。Spring中的几种容器都支持使用XML装配bean,包括:
XMLBeanFactory ,
ClassPathXMLApplicationContext ,
FileSystemXMLApplicationContext ,
XMLWebApplicationContext ;
学习了基本的XML配置包括如下几个方面:
1.添加一个bean
2.设置bean的属性
2.1 手动设置
2.1.1 通过Setter方法
2.1.2 通过构造器
2.2 自动设置
其中bean的属性即为bean里的成员变量,这些成员变量值的获得可以通过setter方法,例如某个属性为name,则setter方法为setName(String name);
或者通过构造器在类被实例化时初始化。Setter方法(例如setName方法)或者构造器的调用都可以通过在XML文件里进行配置,从而实现让spring容器来自动进行。
1)添加一个bean,以下是一个例子:
<bean
id = “mybean”
Class = “blog.spring.MyBean”
Singleton = “false”
init-method = “initMethod”
destroy-method = “destroyMethod”
autowire = “autowire type”
/>
下面是对该标签里各个属性的解释:
Id : 标识该bean的名称,通过factory.getBean(“id”)来获得实例。
Class : 该bean的类路径。
Singleton : 默认为true,即单实例模式,每次getBean(“id”)时获取的都是同一个实例,如果设置为false,即原型模式,则每次获取的是新创建的实例。
Init-method : 在bean实例化后要调用的方法(bean里定义好的方法)。
Destroy-method : bean从容器里删除之前要调用的方法。
Autowire : 其属性要通过何种方法进行属性的自动装配。
对于上述的各个属性,id和class是必要的,其他的则可以省略。例如如果设置了autowire的值,则表明需要自动装配,否则是手动装配。
2)通过Setter方法手动设置bean里的属性
Bean里的属性通过<property>标签来标识。有以下几种情况:
● 简单类型属性
<bean id = “mybean” class = “blog.spring.MyBean”>
<property name = “name”>
<value>springTest</value>
</property>
</bean>
● 引用其他bean
<bean id = “mybean” class = “blog.spring.MyBean” />
<bean id = “mybean1” class = “blog.spring.MyBean1”>
<property name = “name”>
<ref bean = “mybean” />
</property>
</bean>
也可以将<ref>改为
<bean class = “..”>
这样叫做内部bean,缺点是无法在其他地方重用这个bean的实例。
然后今天又试着敲了一遍:
先创建了表: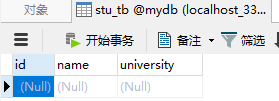
项目结构
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="612049" />
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource">
<ref bean="dataSource"/>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="studentDao" class="Impl.StudentDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate">
<ref bean="jdbcTemplate" />
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
Dao
package Dao;
import Pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
public interface StudentDao {
void addStudent(Student student);
void updateStudent(Student student);
void deleteStudent(int id);
String searchName(int id );
Student searchStudent(int id);
List<Student> findAllStudent();
}
impl
package Impl;
import Dao.StudentDao;
import Pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowCallbackHandler;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate ;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate1 )
{
this.jdbcTemplate =jdbcTemplate1 ;
}
public void addStudent(Student student)
{
String sql="insert into stu_tb values(?,?,?)";
this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,student.getId(),student.getName() ,student.getUniversity() );
}
public void updateStudent(Student student)
{
String sql="update stu_tb set name=?,university=? where id=?";
this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,student.getId(), student.getName(), student.getUniversity());
}
public void deleteStudent(int id)
{
String sql="delete from stu_tb where id=?";
this.jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
}
// 简单查询,按照ID查询,返回字符串
public String searchName(int id)
{
String sql="select name from stu_tb where id=?";
// 返回类型为String(String.class)
return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,String.class,id);
}
public Student searchStudent(int id)
{
String sql="select * from stu_tb";
return this.jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new UserRowMapper(), id);
}
// 复杂查询返回List集合
public List<Student> findAllStudent() {
String sql = "select * from stu_tb";
final List<Student> listAllUser = new ArrayList<Student>();
jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowCallbackHandler() {
public void processRow(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException {
Student u=new Student();
u.setName(resultSet.getString("name"));
u.setUniversity(resultSet.getString("university")) ;
u.setId(resultSet.getString("id"));
listAllUser.add(u);
}
});
return listAllUser ;
//return this.jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new UserRowMapper());
}
}
class UserRowMapper implements RowMapper<Student>
{
//rs为返回结果集,以每行为单位封装着
public Student mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setId(rs.getString("id"));
stu.setName(rs.getString("name"));
stu.setUniversity(rs.getString("university")) ;
return stu;
}
}
student
package Pojo;
public class Student {
private String id;
private String name;
private String university;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String Id) {
this.id = Id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String Name) {
this.name = Name;
}
public String getUniversity () {
return university;
}
public void setUniversity (String University) {
this.university = University;
}
public String toString(){
return "[ID"+id+"Name"+name+"University"+university+"]";
}
}
跟着写了一个测试类
import Dao.StudentDao;
import Pojo.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import java.util.List;
public class StudentTest {
@Test
public void add()
{
Student stu=new Student();
stu.setId("1");
stu.setName("张三");
stu.setUniversity("清华");
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
dao.addStudent(stu);
}
@Test
public void add2()
{
Student stu=new Student();
stu.setId("2");
stu.setName("李四");
stu.setUniversity("复旦");
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
dao.addStudent(stu);
}
@Test
public void update()
{
Student stu=new Student();
stu.setId("1");
stu.setName("ssssss");
stu.setUniversity("dddddd");
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
dao.updateStudent(stu) ;
}
@Test//删
public void delete(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
dao.deleteStudent(1);
}
@Test//查(复杂查询,返回对象集合)
public void search2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
List<Student> list=dao.findAllStudent();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
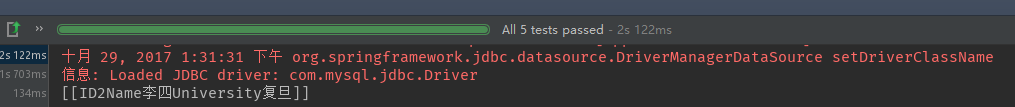
测试结果
遇到的疑惑
1,为什么这段代码没有修改成功
public void update()
{
Student stu=new Student();
stu.setId("1");
stu.setName("ssssss");
stu.setUniversity("dddddd");
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
StudentDao dao=(StudentDao) applicationContext.getBean("studentDao");
dao.updateStudent(stu) ;
}
表还是原来的数据、
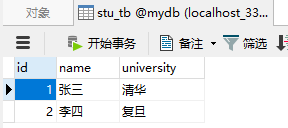
2,这些红色的信息是什么鬼,怎么来的
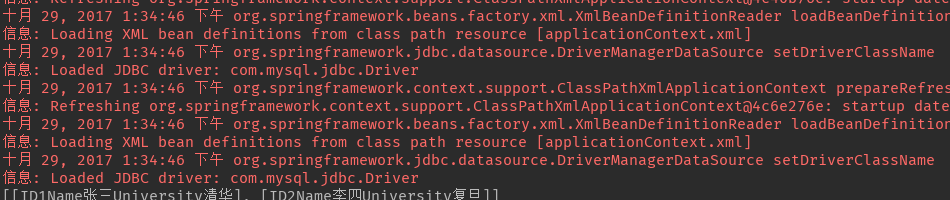
3,
<bean id="studentDao" class="Impl.StudentDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate">
<ref bean="jdbcTemplate" />
</property>
id是这个bean的标识,class是这个bean的类路径。
那下面的
<property name="jdbcTemplate">
和
<ref bean="jdbcTemplate" />
代表的是什么呢??一直没搞懂,,
明日计划
我觉的是不是可以看mybatis了,卡死了好多天了。
收获
感觉提高了对jdbcTemplate的了解,从它的配置以及实现的原理。





评论