发表于: 2017-07-05 22:47:41
1 1163
今天完成的事情:
1. 学习IOC容器
可以分为:Spring BeanFactory 容器和Spring ApplicationContext 容器包括 BeanFactory 容器的所有功能
ApplicationContext 容器包括 BeanFactory 容器的所有功能
2. Bean的定义、作用域、生命周期和后置处理器
bean 是一个被实例化,组装,并通过 Spring IoC 容器所管理的对象
3. 基于构造方法的依赖注入和基于构造函数的依赖注入
两者区别在于配置元数据beans.xml中的
constructor-arg:通过构造函数注入。
property:通过构造方法注入
明天计划的事情:
1.spring 基于注解的配置
2. spring 下使用 Log4J 记录日志
3. 看看其他师兄的上品日报怎么写的,学习学习。
遇到的问题:
1. 生成的的 getBean() 方法得到所需要的 bean,通过配置文件中的 Beans ID 来返回一个真正的对象,这个对象是什么,
是<bean>中实例化类后的对象吗?
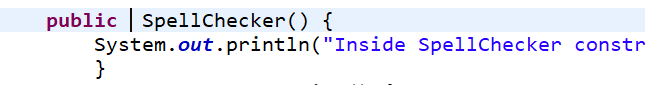
2. 在下图的类中的方法为何不能加void,加了就不能输出下面的语句
(下文贴有代码)
收获:
1. 作用域
<bean>标签中
singleton
Spring IoC 容器刚好创建一个由该 bean 定义的对象的实例。
即若有复数context.getBean实例化时,所有的实例化对象指向同一个对象的实例
prototype
那么每次特定的 bean 发出请求时 Spring IoC 容器就创建对象的新的 Bean 实例
即若有复数context.getBean实例化时,每一个都指向各自的对象的实例,互不相干
2. Bean 的生命周期
<bean>标签中
init-method = "inti"
在实例化 bean后,立即调用该方法
public void init(){
}
destroy-method = "destroy"
destroy-method 指定一个方法,只有从容器中移除 bean 之后,立即调用该方法
public void destroy(){
}
3. Bean 后置处理器
BeanPostProcessor 接口定义回调方法, ApplicationContext 会自动检测由 BeanPostProcessor 接口的实现定义的 bean,
注册这些 bean 为后置处理器,然后通过在容器中创建 bean,在适当的时候调用它
postProcessBeforeInitialization 在处理bean之前执行
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("BeforeInitialization : " + beanName);
return bean;
}
postProcessAfterInitialization 在实例化bean后立即执行,(在destroy-method后执行)
注: 3和4 需要在 AbstractApplicationContext 类中声明 registerShutdownHook() 的关闭
context.registerShutdownHook();
4. 基于设值函数的依赖注入的实例
这次spring 是直接用jar包的形式引进来
文件结构:
MainApp.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MainApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 制定容器ApplicationContext
* 生成工厂对象。加载完指定路径下 Beans 配置文件后
* 利用框架提供的 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext API 去生成工厂 bean。
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 负责生成和初始化所有的对象,
* 所有在 XML bean 配置文件中的 bean。
*/
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Beans.xml");
/*
* 利用生成的的 getBean() 方法得到所需要的 bean。
* 这个方法通过配置文件中的 Beans ID 来返回一个真正的对象。
* 一旦得到这个对象,就可以利用这个对象来调用任何方法。
*/
TextEditor te = (TextEditor) context.getBean("textEditor");
te.spellCheck();
}
}
SpellChecker.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class SpellChecker {
public SpellChecker() {
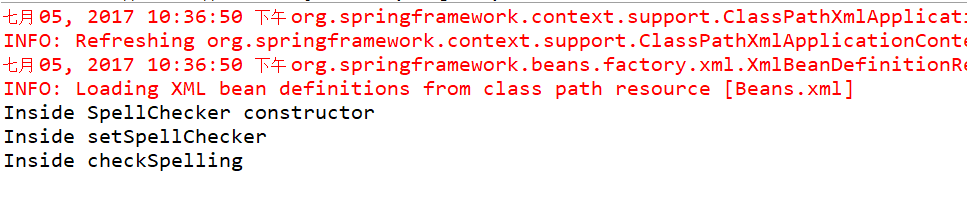
System.out.println("Inside SpellChecker constructor");
}
public void checkSpelling() {
System.out.println("Inside checkSpelling");
}
}
TextEditor.java
package com.tutorialspoint;
public class TextEditor {
private SpellChecker spellChecker;
//一种注入依赖关系的setter方法
public void setSpellChecker(SpellChecker spellChecker) {
System.out.println("Inside setSpellChecker");
this.spellChecker = spellChecker;
}
//一个getter方法来返回spellChecker
public SpellChecker getSpellChecker() {
return spellChecker;
}
public void spellCheck() {
spellChecker.checkSpelling();
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!--class :指定用来创建 bean 的 bean 类
name/id: 这个属性指定唯一的 bean 标识符
可以看出依赖关系,textEditor依赖spellChecker-->
<bean id="textEditor" class="com.tutorialspoint.TextEditor">
<property name="spellChecker" ref="spellChecker"/>
</bean>
<bean id="spellChecker" class="com.tutorialspoint.SpellChecker">
</bean>
</beans>
结果:
参考资料:
Spring - constructor-arg和property的使用示例
Spring的两种依赖注入方式:setter方法注入与构造方法注入
Spring 教程
PS:基础不牢地动山摇,很多概念看不懂,还得回头补一补






评论