发表于: 2017-06-15 14:47:43
1 1327
今天完成的事:
前面做任务对配置文件都是一知半解的,今天特意对配置文件做一个梳理。什么配置应该在什么位置,配置文件代表的意义。
web.xml文件:web请求的入口
1,定义头和根元素(大小写敏感)
a,必须以xml头开始 b,DOCYTPE紧跟其后 c,web-app
2,部署描述符文件内的顺序。(一共有21项,但平时接触的大概就四五项,所以以经常遇到的作为重点)
web.xml加载顺序:<context-param> <listener> <filter> <servlet>
<context-param>:加载spring等的配置文件,多个配置文件用“,”隔开。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring-mybatis.xml,classpath:memcached.xml,classpath:spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>:通过ContextLoaderListener在web-app初始化时,获取ContextConfigLocation里面的配置文件,进行相关文件的初始化。
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>:filter是“加强版”的servlet,而servlet里面有request和response两个对象,filter对用户请求进行预处理,接着将HttpServletRequest请求交给servlet进行处理并生成响应,最后再对服务器响应HttpServletResponse进行后处理。
<filter-mapping>:用来声明web应用的过滤器映射,过滤器被映射到一个servlet或URL路径。
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<servlet>:服务端小程序。这里配置的是DispacherServlet,所有的请求都要经过它。<servlet>与<servlet-mapping>中的<servlet-name>名字要一致。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- spring mvc的配置文件 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>mvc-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
网上找了个ContextLoaderListener和DispactherServlet初始化上下文关系和区别:
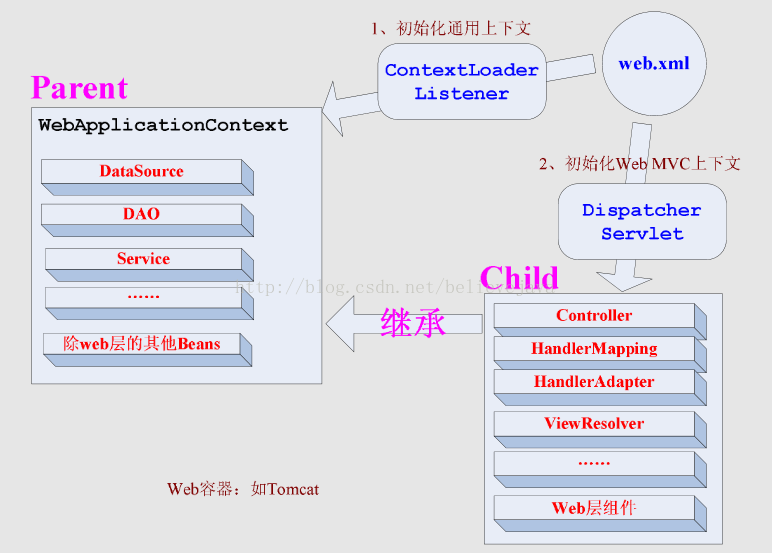
从图中也可以看到,ContextLoaderListener初始化的上下文加载的Bean是对整个应用程序共享的,如DAO层,Service层的Bean,DispactherServlet初始化的上下文加载的Bean是只对SpringMVC的Bean。其实从配置文件中也可以看出来区别。
ApplicationContext.xml文件:
这个是spring的配置文件。
1,通过注解,将service的生命周期纳入spring的管理(我看另外一篇文章说,开启自动扫描的话就不需要注解了)
<context:annotation-config/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lyyone.service" />
2,配置数据源,这里最好使用引入jdbc.properties的方式将数据源与spring解耦。
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/classroom?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8"/>
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="123456" />
</bean>
3,扫描映射存放SQL语句的映射文件,把数据源注入给sessionFactory
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:*Mapping.xml"/>
</bean>
4,扫描Mapper,将其纳入spring生命周期管理。
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lyyone.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
SpringMVC.xml
1,扫描Controller,并将其生命周期纳入spring管理
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- 扫描web相关的controller -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.lyyone.controller">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
2,注解驱动
<!-- 注解驱动 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
3,静态资源如HTML,css,js,图片等可以被访问
<!-- 静态页面访问 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler />
4,视图解析器。
<!-- 视图解析器 -->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="viewClass" value="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView" />
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/layout/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
<property name="order" value="2"/>
</bean>
把师兄的代码再敲一遍,看看与自己的有何不同。还在继续。。
明日计划:
继续昨天未完成的,学习任务八知识点。
遇到的问题:
暂无。
收获:
之前看师兄的代码,看到他的数据库id字段是用的Long型,还以为是错了。昨天敲代码时特意查了下。原来Long是对long的包装,正如Integer是对int的包装一样。
<mapper namespace="com.ptteng.dao.StudentDao" >
<resultMap id="studentMap" type="com.ptteng.model.Student" >
<id property="id" column="id" javaType="java.lang.Long" jdbcType="Integer" ></id>
<result property="name" column="name" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result property="avatar" column="avatar" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result property="type" column="type" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
<result property="introduction" column="introduction" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
</resultMap>
<select id="select" resultMap="studentMap" >
select * from student
</select>
</mapper>
在映射文件中是这样配置的。
Long叫做long的包装类。在Java中,有时候运算必须在两个类之间记性,不允许类和数字之间运算。所以就把数字包装成为一个对象。





评论