发表于: 2020-08-24 23:17:10
1 2350
今天完成的事情
1.mybatis 注解 script 标签
2.@RequestParam @PathParam @PathVariable等注解区别
3.@CookieValue @RequestHeader @RequestMapping 及其属性
4.SQL 过滤数据
收获
1. mybatis script 标签
要在带注解的映射器接口类中使用动态 SQL,可以使用 script 元素。比如:
@Insert(
"<script>"
+ "insert into t_coffee"
+ "<trim prefix='(' suffixOverrides=',' suffix=', create_time, update_time)'>"
+ " <if test='name != null'> name, </if>"
+ " <if test='price != null'> price, </if>"
+ "</trim>"
+ "<trim prefix='values (' suffixOverrides=',' suffix=', now(), now() )'>"
+ " <if test='name != null'> #{name, jdbcType=VARCHAR}, </if>"
+ " <if test='price != null'> #{price, jdbcType=BIGINT}, </if>"
+ "</trim>"
+ "</script>"
)
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true)
int saveSelective(Coffee coffee);
写好 script 标签之后内部的其他标签就和 xml 文件的一样了。
查看了一下 mybatis 的注解包,还有挺多其他的注解的,可以完成 resultSet resultMap 的功能,总之先知道有这个东西,之后慢慢了解。
2. Spring MVC 的部分注解
- defaultValue 取不到参数或者参数为空则启用默认值
- name 绑定本次参数的名称(不加这个属性则默认 URL 上的参数名称与注解的参数名称一致,否则可以使用 name 属性修改)
- value 和 name 属性一样。是 name 的一个别名
- required 设置为 ture 的时候这个属性是必须有的
- name 绑定本次参数的名称(不加这个属性则默认 URL 上的参数名称与注解的参数名称一致,否则可以使用 name 属性修改)
- value 和 name 属性一致
- Required 设置为 ture 的时候这个属性是必须的
- @Controller
- @SessionAttributes(value="currentUser")
- public class SessionAttributesController {
- @RequestMapping("/session/attributes/{id}/{name}")
- public ModelAndView sessionAttributes(@PathVariable Integer id,@PathVariable String name){
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("session");
- mav.addObject("currentUser", new User(id,name));
- return mav;
- }
- }
- @Controller
- @SessionAttributes(value={"currentUser","saveTime"},types={User.class,Date.class})
- public class SessionAttributesController {
- @RequestMapping("/session/attributes/{id}/{name}")
- public ModelAndView sessionAttributes(@PathVariable Integer id,@PathVariable String name){
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("session");
- mav.addObject("currentUser", new User(id,name));
- mav.addObject("saveTime", new Date());
- return mav;
- }
- @RequestMapping("/session/attributes/test")
- public ModelAndView sessionAttributesage(@ModelAttribute("currentUser") User u,@ModelAttribute("saveTime") Date d){
- System.out.println(u.getUsername());
- System.out.println(d);
- ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("session");
- return mav;
- }
- }
@RequestParam 从请求内取值,@PathVariable 是从 URL 模板内取值。
http://example.org/goods?name=apple
goods 就属于 URL 模板取值(@PathVariable),问号后面的 name 属于请求内的值(@RequestParam)
@RequestParam 有如下四个参数:
@PathVariable 有如下属性
@CookieValue 这个注解用于取出对应 cookie 的值绑定到指定方法
public void cookieValueTest(@CookieValue(value = "JSESSIONID", defaultValue = "") String sessionId)
在上面这一段代码中,我们把名为 JSESSIONID 的 cookie 取出来放到 sessionId 这个变量中,如果我们没有取到这个 cookie 的话就赋一个默认值 "" 给 sessionId
@RequestHeader 可以把Request请求header部分的值绑定到方法的参数上。
@RequestMapping("/displayHeaderInfo.do")
public void displayHeaderInfo(@RequestHeader("Accept-Encoding") String encoding,
@RequestHeader("Keep-Alive") long keepAlive) {
}
上面的代码,把request header部分的Accept-Encoding的值,绑定到参数encoding上了, Keep-Alive header的值绑定到参数keepAlive上。
@RequestParam
A)常用来处理简单类型的绑定,通过Request.getParameter()获取的String可直接转换为简单类型的情况( String-->简单类型的转换操作由ConversionService配置的转换器来完成);因为使用request.getParameter()方式获取参数,所以可以处理get方式中queryString的值,也可以处理post方式中 body data的值;
B)用来处理Content-Type: 为application/x-www-form-urlencoded编码的内容,提交方式GET、POST;
C)该注解有两个属性:value、required;value用来指定要传入值的id名称,required用来指示参数是否必须绑定;
@SessionAttributes 这个注解可以很方便的往请求中添加我们需要的 session 数据
SessionAttributes是只能注解于类或者接口,@SessionAttributes的value代表我们需要把什么样的对象放入session,在我们的方法后当我们把对象放入ModelMap这个对象的时候,如果给出的key也会自动放入session的
在这个例子中我们往 ModelAndView 插入的与 注解中同名的对象将会被插入到 session 中。之后再其他的地方我们就可以获取到 session 的内容进行处理。
在下面这个例子中,使用 @SessionSttributes 注解配合 @ModelAttributes 注解写入与获取 session 数据。
3. SQL 过滤数据
在 SELECT 使用 WHERE 子句指定搜索条件进行过滤。
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price=3;
仅返回价格为 3 的商品信息。
WHERE 子句部分操作符:
<> 不等于
!= 不等于
!< 不小于
!> 不大于
BETWEEN AND 在指定的两个值之间
IS NULL null 值
检查单个值
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price<3;
不匹配检查
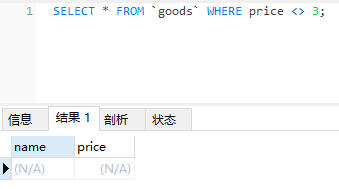
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price <> 3;
范围值检查
检查值的范围要使用 BETWEEN 操作符
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price BETWEEN 3 AND 5;
空值检查
判空在 SQL 中有一个特定的判断符 IS NULL,而不是使用 != NULL
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price IS NULL;
通过 WHERE 子句过滤不包含指定值的所有行的时候是没法返回 null 值的行的。
例如以下数据
INSERT INTO goods (name, price) VALUES("apple", null);
SELECT name, price
FROM goods
WHERE price != 3;
这个时候上面插入的这一条数据不会被返回。






评论