发表于: 2020-07-27 21:57:55
1 2030
今天完成的事:
看了下之前师兄的总结,了解了Spring RMI
RMI全称是Remote Method Invocation-远程方法调用,是纯Java的网络分布式应用系统的核心解决方案之一。Java RMI 支持存储于不同地址空间的程序级对象之间彼此进行通信,实现远程对象之间的无缝远程调用。
RMI目前使用Java远程消息交换协议JRMP进行通信。由于JRMP是专为Java对象制定的,用Java RMI开发的应用系统可以部署在任何支持JRE的平台上。但由于JRMP是专为Java对象制定的,因此,RMI对于用非Java语言开发的应用系统的支持不足。不能与用非Java语言书写的对象进行通信。
一个正常工作的RMI系统由下面几个部分组成:
1·远程服务的接口定义
2·远程服务接口的具体实现
3·桩(Stub)和框架(Skeleton)文件
4·一个运行远程服务的服务器
5·一个RMI命名服务,它允许客户端去发现这个远程服务
6·类文件的提供者(一个HTTP或者FTP服务器)
7·一个需要这个远程服务的客户端程序
RMI的主要优点:
1. RMI是Java编写的, 具有 “编写一次,到处运行 ” 的特性。任何基于RMI的系统均可100%地移植到 任何Java虚拟机上
2. 面向对象:RMI可将完整的对象作为参数和返回值进行传递直接通过网络传输对象数据。
3.可移动属性:RMI可将属性从客户机移动到服务器,或者从服务器移到客户机。
4.设计方式:对象传递功能使您可以在分布式计算中充分利用面向对象技术的强大功能。
5.安 全:RMI使用Java内置的安全机制保证下载执行程序时用户系统的安全。
分布式和集群
分布式:一个业务分拆多个子业务,部署在不同的服务器上。集群:同一个业务,部署在多个服务器上
RMI需要服务端和客户端
下面写一个测试
先写服务端,新建一个maven工程
定义一个接口
public interface ServerRmi {
public String sayHi(String name);
}
接口的实现类
public class ServerRmiImpl implements ServerRmi{
@Override
public String sayHi(String name) {
return "Hi,"+name;
}
}
服务端启动程序
public class Testrun {
public static void main(String[] args){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
context.getBean("serverTest");
System.out.println("RMI启动就绪");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"
default-autowire="byName" default-lazy-init="true">
<!-- RMI服务端 -->
<!-- RMI服务端远程接口实现类 -->
<bean name="rmiserver" class="com.ptt.service.ServerRmiImpl"/>
<bean name="serverTest" class="org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiServiceExporter">
<!-- 将远程接口实现类对象设置到RMI服务中 -->
<property name="service" ref="rmiserver"/>
<!-- 设置RMI服务名,为RMI客户端依据此服务名获取远程接口实现类对象引用奠定基础 -->
<property name="serviceName" value="serverRmiTest"/>
<!-- 将远程接口设置为RMI服务接口 -->
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.ptt.service.ServerRmi"/>
<!-- service本地实现,serviceName对外提供的名称对外提供的名称,registyPort开启端口 -->
<property name="registryPort" value="1021"/>
</bean>
</beans>
说明:service本地实现,serviceName对外提供的名称对外提供的名称,registyPort开启端口
编写客户端
重建一个maven工程
定义一个对应的接口
public interface ServerRmi {
public String sayHi(String name);
}
编写测试方法
public class TestRun {
public static void main(String[] args){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
ServerRmi rmi = (ServerRmi) context.getBean("clentrmi");
System.out.println(rmi.sayHi("rmi"));
}
编写配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd"
default-autowire="byName" default-lazy-init="true">
<bean name="clentrmi" class="org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="serviceUrl" value="rmi://127.0.0.1:1021/serverRmiTest"/>
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.ptt.service.ServerRmi"/>
</bean>
先启动服务器程序
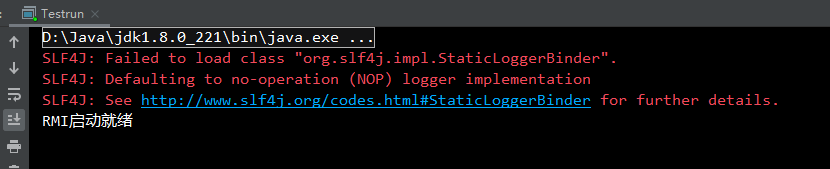
启动客户端程序,成功输出
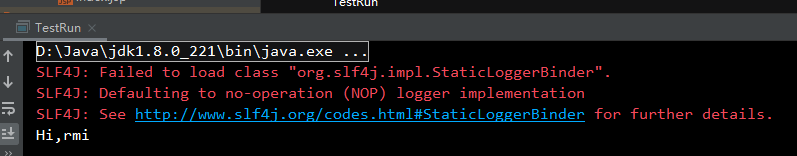
接下来测试之前的报名系统
直接在服务端xml配置文件中添加配置
<!-- RMI服务端 -->
<!-- RMI服务端远程接口实现类 -->
<bean name="bmbService" class="com.ptt.service.BmbServiceImpl" scope="prototype"/>
<bean name="rmiserver" class="org.springframework.remoting.rmi.RmiServiceExporter">
<!-- 将远程接口实现类对象设置到RMI服务中 -->
<property name="service" ref="bmbService"/>
<!-- 设置RMI服务名,为RMI客户端依据此服务名获取远程接口实现类对象引用奠定基础 -->
<property name="serviceName" value="BmbServiceImpl"/>
<!-- 将远程接口设置为RMI服务接口 -->
<property name="serviceInterface" value="com.ptt.service.BmbService"/>
<!-- 为RMI服务端远程对象注册表设置端口号-->
<property name="registryPort" value="1022"/>
</bean>
编写服务端启动程序
public class TestRun {
public static void main(String[] args){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
context.getBean("rmiserver");
System.out.println("RMI启动");
}
}
重建一个maven工程,编写客户端
编写一个对应的实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Bmb implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String qq;
private String type;
private String jointime;
private String school;
private String studyid;
private String dailylink;
private String hope;
private Timestamp create_at;
private Timestamp update_at;
}
编写一个对应的接口
public interface BmbService {
/**
* 添加用户
*/
int saveBmb(Bmb bmb);
/**
* 根据id删除用户
*/
int deleteBmbById(Integer id);
/**
* 修改用户
*/
int updateBmb(Bmb bmb);
/**
* 根据id查询单个用户
*/
Bmb getBmbById(Integer id);
/**
* 查询所有操作
*/
List<Bmb> queryAllBmb();
}
编写测试程序
public static void main(String[] args){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
BmbService bmbService = (BmbService) context.getBean("rmiProxyFactoryBean");
System.out.println(bmbService.getBmbById(5));
}
先启动服务端
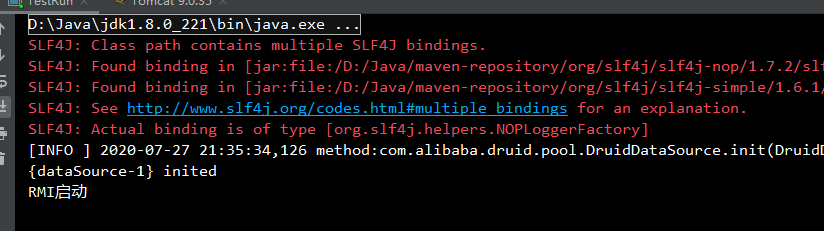
启动客户端测试程序
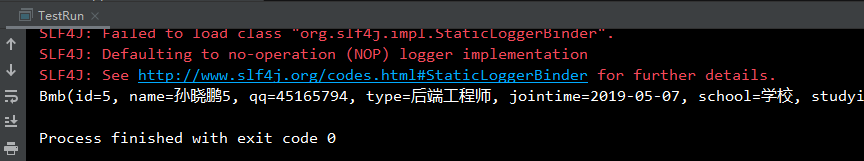
成功输出结果
后面只需要将每个接口都配置一个bean对象即可
明天计划的事:完成service和web的分离
遇到的困难:







评论