发表于: 2020-01-05 19:00:26
1 1246
啥也不说就是干!!!
今天完成的事情:
1、添加统一登录验证的拦截器
在使用 SpringMVC 的时候,可以使用 HandlerInterceptor,拦截 SpringMVC 处理请求过程,自定义前置和处理逻辑,比如:
日志拦截器:记录请求和响应。这样就可以知道每一次请求的参数,响应结果,执行的时长等信息
认证拦截器:可以解析前端传入的用户标识,例如 access_token 访问令牌,获得当前用户的信息,记录到 ThreadLocal 中。这样,后续的逻辑只要通过 ThreadLocal 就可以获取用户信息
授权拦截器:可以通过每个 API 接口需要的授权信息,进行判断当前请求是否允许访问。例如:用户是否登陆,是否有该 API 的操作权限等
限流拦截器:可以通过每个 API 接口的限流配置,进行判断当前请求是否超过允许的请求频率,避免恶意请求
HandlerInterceptor 接口,定义了三个拦截点:
// HandlerInterceptor.java
public interface HandlerInterceptor {
default boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return true;
}
default void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
default void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
@Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception {
}
}
1)自定义拦截器需要继承 HandlerInterceptor:LoginInterceptor
public class LoginInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Autowired
StudentService studentService;
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o) throws Exception {
String url = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI();
if (url.contains("/u")) {
if (httpServletRequest.getSession().getAttribute("student") != null) {
return true;
} else {
// request.getRequestDispatcher("/login.jsp").forward(servletRequest,servletResponse);
//进行自动登录
String cookie = CookieUtils.getCookie(httpServletRequest, "token");
if (cookie != null) {
String token = DesUtils.decode(cookie);
long id = Long.parseLong(token.split(",")[0]);
Student student = studentService.queryStudentInfoById(id);
httpServletRequest.getSession().setAttribute("student", student);
System.out.println(student);
return true;
} else {
httpServletResponse.sendRedirect(httpServletRequest.getContextPath() + "/login.jsp");
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
}
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, Object o, Exception e) throws Exception {
}
}
在 preHandle 里面判断 session 中是否包含了登录信息,如果有直接放行。没有的话就从 request cookie 中取出 token,拿到用户 id查询出用户信息,然后放入 session 中。
2)对需要登录访问的 url 统一加上 /u 前缀
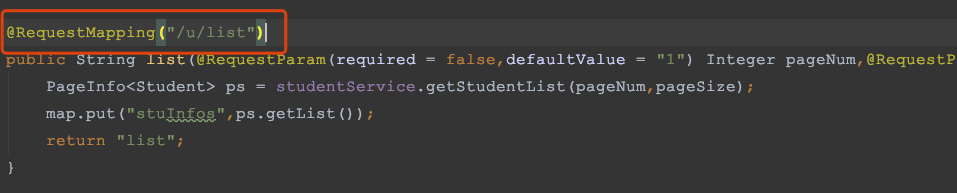
对于任务四中的两个页面,其中第一个页面不需要登录,第二个页面需要登录才能访问,所以在访问第二个页面的请求中加 /u
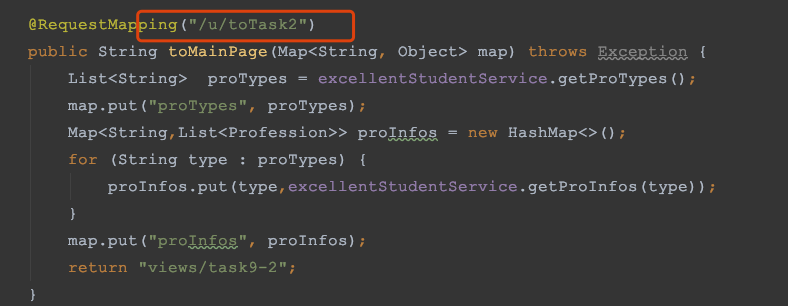
3) 在 SpringMVC 配置文件中配置拦截器的拦截规则
<!-- 配置拦截器 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!-- 多个拦截器,按顺序执行 -->
<mvc:interceptor>
<!--<mvc:mapping path="/**"/> <!– 拦截所有的url包括子url路径 –>-->
<mvc:mapping path="/student/u/**"/> <!-- 拦截所有的url包括子url路径 -->
<bean class="com.gerry.jnshu.interceptor.LoginInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
<!-- 其他拦截器 -->
</mvc:interceptors>
启动项目进行测试
输入 http://localhost:8080/u/list 进行访问,未登录就重定向到登录页面
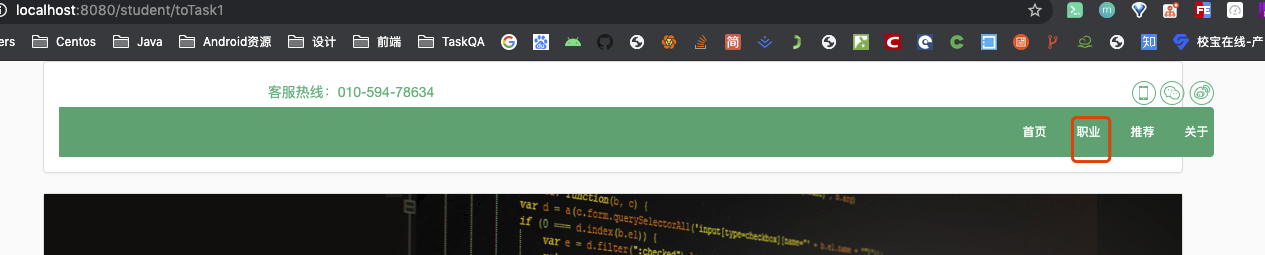
点击职业跳到第二个页面未登录的话会重定向到登录页
2、Java中常见的加密算法
加密算法种类:单向加密、对称加密、非对称加密
单向加密:
1)Base64:从二进制到字符的过程,用 64 个字符来表示任意的二进制数据,常用于 HTTP 加密,图片编码传输等
可打印字符:在 ASCII 码中规定,0-31、128这个33个字符属于控制字符,32-127 这95个字符属于可打印字符
转换方式:在 HTTP 协议下传输二进制数据时需要将其转换为字符数据,而网络传输只能传输可打印字符(95个),不能转换的就需要使用 Base64 进行转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 编码
String encode = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString("son".getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println(encode); // c29u
// 解码
byte[] decode = Base64.getDecoder().decode("c29u");
System.out.println(new String(decode, "UTF-8"));
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2)MD5:一般用于确保信息的传输完整一致性,校验传输的数据是否被修改,一旦原始信息被修改,生成的 MD5 值回表的很不同
3)SHA 家族:是一个密码三列函数家族,是 FIPS 所认证的安全三列算法。跟 MD5 类似,都是对文本进行散列,产生一定长度的散列值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "you are my son"; // 原文
try {
byte[] a;
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
a = messageDigest.digest(content.getBytes());
System.out.println(byte2hex(a)); // 333a9634d8809b5a9e8d280d82553b8fd8d4a911
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
a = messageDigest.digest(content.getBytes());
System.out.println(byte2hex(a)); // cdb2c97079d9a1943eea98de4201f5c4f49ecda5af2b364e1c7a5d1ae89688eb
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
a = messageDigest.digest(content.getBytes());
System.out.println(byte2hex(a)); // 6fe6b9a8f8bd29f4f4f1368a0619a7ae
// 第三方 MD5 算法。需要添加 jar 包 org.apache.commons.codec.digest.DigestUtils
String encodeStr=DigestUtils.md5Hex(content);
System.out.println(encodeStr); // 6fe6b9a8f8bd29f4f4f1368a0619a7ae
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static String byte2hex(byte[] b) {
String hs = "";
String stmp = "";
for (int n = 0; n < b.length; n++) {
stmp = (java.lang.Integer.toHexString(b[n] & 0XFF));
if (stmp.length() == 1) {
hs = hs + "0" + stmp;
} else {
hs = hs + stmp;
}
}
return hs;
}
对称加密:对称加密的意思就是信息收发都有相同的一把钥匙,消息的加密解密都用这进行
DES:数据加密标准,速度较快。适用于加密大量数据的场合
/**
* 加密
*
* @param content
* 待加密内容
* @param key
* 加密的密钥
* @return
*/
public static byte[] encrypt(String content, String key) {
try {
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
DESKeySpec desKey = new DESKeySpec(key.getBytes());
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
SecretKey securekey = keyFactory.generateSecret(desKey);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, securekey, random);
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes());
return result;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
/**
* 解密
*
* @param content
* 待解密内容
* @param key
* 解密的密钥
* @return
*/
public static String decrypt(byte[] content, String key) {
try {
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
DESKeySpec desKey = new DESKeySpec(key.getBytes());
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
SecretKey securekey = keyFactory.generateSecret(desKey);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, securekey, random);
byte[] result = cipher.doFinal(content);
return new String(result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
非对称加密:一种密钥的保密方法。非对称加密算法需要两个密钥:公钥(publickey)和私钥(privatekey)。公钥与私钥是一对,如果用公钥对数据进行加密,只有用对应的私钥才能解密,如果用私钥对数据进行加密,那么只有用对应的公钥才能解密
RSA:这种算法非常可靠,密钥越长破解越难
public static final String RSA_ALGORITHM = "RSA";
public static final Charset UTF8 = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception {
// generate public and private keys
KeyPair keyPair = buildKeyPair();
PublicKey publicKey = keyPair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = keyPair.getPrivate();
// encrypt the message
byte [] encrypted = encrypt(privateKey, "This is a secret message");
System.out.println(base64Encode(encrypted)); // <<encrypted message>>
// decrypt the message
byte[] secret = decrypt(publicKey, encrypted);
System.out.println(new String(secret, UTF8)); // This is a secret message
}
public static KeyPair buildKeyPair() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
final int keySize = 2048;
KeyPairGenerator keyPairGenerator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
keyPairGenerator.initialize(keySize);
return keyPairGenerator.genKeyPair();
}
public static byte[] encrypt(PrivateKey privateKey, String message) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, privateKey);
return cipher.doFinal(message.getBytes(UTF8));
}
可以将生成的公钥和私钥保存至文件中
public static byte[] decrypt(PublicKey publicKey, byte [] encrypted) throws Exception {
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, publicKey);
return cipher.doFinal(encrypted);
}
public static String base64Encode(byte[] data) {
return new BASE64Encoder().encode(data);
}
public static byte[] base64Decode(String data) throws IOException {
return new BASE64Decoder().decodeBuffer(data);
}
/**
* 从字符串中加载公钥
*
*/
public static RSAPublicKey loadPublicKey(String publicKeyStr) throws Exception {
try {
byte[] buffer = base64Decode(publicKeyStr);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(buffer);
return (RSAPublicKey) keyFactory.generatePublic(keySpec);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static RSAPrivateKey loadPrivateKey(String privateKeyStr) throws Exception {
try {
byte[] buffer = base64Decode(privateKeyStr);
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(buffer);
KeyFactory keyFactory = KeyFactory.getInstance(RSA_ALGORITHM);
return (RSAPrivateKey) keyFactory.generatePrivate(keySpec);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void savePublicKey(PublicKey publicKey) throws IOException {
// 得到公钥字符串
String publicKeyString = base64Encode(publicKey.getEncoded());
System.out.println("publicKeyString="+publicKeyString);
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("publicKey.keystore");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
bw.write(publicKeyString);
bw.close();
}
public void savePrivateKey(PrivateKey privateKey) throws IOException {
// 得到私钥字符串
String privateKeyString = base64Encode(privateKey.getEncoded());
System.out.println("privateKeyString="+privateKeyString);
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("privateKey.keystore"));
bw.write(privateKeyString);
bw.close();
}
以上就是常用的 Java 加密算法实现
明天计划的事情:
任务5的深度思考及提交任务5
遇到的问题:
暂无
收获:
学习了SprignMVC 拦截器及配置,java 常见的加密算法实现





评论